HTML
What is HTML
Introduction
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a series of elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><title> My first page </title></head><body><h1>Main heading</h1></body></html>
Doctype: Declaration in the document of which version of the HTML standard is following The declaration is not an HTML tag. It is an "information" to the browser about what document type to expect. In HTML 5, the declaration is simple:
<!DOCTYPE html>html : Root element which wraps our whole document
head : It contains document metadata(used by the browsers or search engines), related documents, links
body : It contains document data which is displayed in the browser
Click here to validate your HTML code.
Anatomy of an HTML element

head element
It is primartily about metadata, the information that is used by the browser or search engine and not necessarily displayed to the user.
- title : Title of the document. It is also used in the search engine optimisation.
element
- Use longer tiles(avoid one or two words)
- Search engines will display 50-60 characteres, so not to have more than that.
- meta : Allows to specify the metadata of the document(information about the author etc). It is used by the browser, search engines or othe web services.
- script: Specifies the script
- style : Defines the style to apply to the body of the document
- link : Indicates some related docments
body element
It defines the body of the document. It includes all the contents of an HTML document, such as headings, texts, list, links, tables, images etc.
id v/s class
ID
- ID's are unique.
- Each element can have only one ID
- Each page can have only one element with that ID
Class
- Classes are not unique
- We can used multiple class on same element or same class on multiple elements
Headings
These are important for SEO. Search engines use the headings to index the structure and content of your web pages.
H1
- Primary heading of the document
- Used by search engines - should include one in a page
H2-H6
- H2 defines a less important heading than h1 and h6 is the least important heading.
Lists
Unordered list
Bullet list. List them with some bullet to the left side.
<ul><li>Coffee</li><li>Tea</li><li>Milk</li></ul>
Ordered list
Items are marked with numbers or alpha labels.
<ol><li>Coffee</li><li>Tea</li><li>Milk</li></ol>
If you want to know about nested lists, or how to change the marker style, click here
Anchors
The <a> tag defines a hyperlink, which is used to link from one page to another. Anchors act as either source or target for linking.
- Named anchors are targets.
- Anchors with href are sources
HTML5 Structural elements
Basically the structural elements are used to divide the web pages into logical parts that are descriptive of the type of content they contain. Like a document, a webpage contains headers, footers, articles etc.
These are used to describe the content to the search engine
main
It is used to wrap the main content of the page. It tells the search engine that the most important information regarding the search relevant is in this element. You can only add one main element in a page.
article
It comes inside the main element. It is way to group content together and signalling the search engine that the content inside is important. You can add more article element in a page.
aside
Defines a block of content that is related to the main content around it, but not central to the flow of it. The information that is not crucial to be displayed in the webpage can be surrounded by this element. i.e., Defines content aside from the content (like a sidebar)
section
We can use this element when we want to group contents in a logical way. It is similar to div element. Used to either group different articles into different purposes or subjects, or to define the different sections of a single article.
header
Used to contain the header of a site
footer
Used to contain the footer of a site
nav
Logical container for site navigation. It contains the navigation functionality for the page.
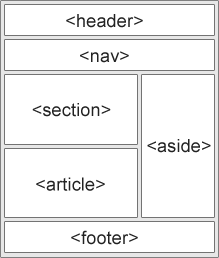
<html><body><header><nav>....</nav></header><main><article><section>... </section><aside>... </aside></article></main></body></html>
time
Used for marking up times and dates.
figure and figcaption
Used to encapsulate a figure as a single item, and contain a caption for the figure, respectively.
details and summary
<details>- Defines additional details<summary>- Defines a heading for the<details>element
Reference :
HTML Layout Technique - CSS Flexbox Layout
Before the Flexbox Layout module, there were four layout modes:
- Block, for sections in a webpage
- Inline, for text
- Table, for two-dimensional table data
- Positioned, for explicit position of an element
The Flexible Box Layout Module, makes it easier to design flexible responsive layout structure without using float or positioning.
Use of flexbox ensures that elements behave predictably when the page layout must accommodate different screen sizes and different display devices.
Reference :